[3xn 타일링]
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/12902
코딩테스트 연습 - 3 x n 타일링
programmers.co.kr
* 조건
- 세로의 길이가 3이고 가로의 길이가 n인 바닥이 존재한다
- 타일을 채울 때, 가로 또는 세로 형태로 배치할 수 있다
- 가로 또는 세로의 최대 길이는 2이다
- 경우의 수가 많은 것을 대비해 경우의 수를 1,000,000,007으로 나눈 나머지를 return 한다
* 알고리즘
- DP
* 로직(Logic)
- 우선 홀수인 경우에는 답을 구할 수 없다
- 짝수인 경우를 고려했을 때,
if) n=2
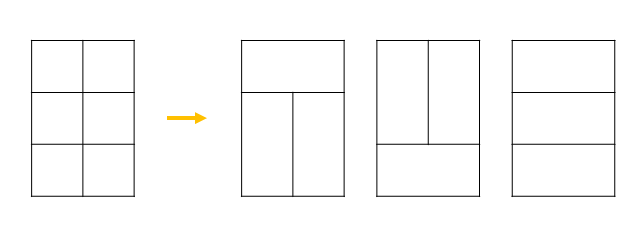
: 3개
if) n=4
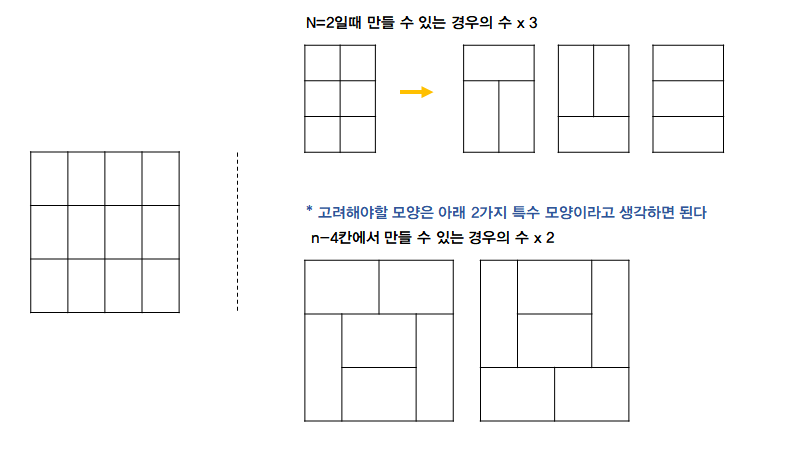
: (3 * 3) + 2 = 11
- 이런식으로 나열해보면 규칙을 찾을 수 있게된다
- 이전 n이 만들어낼 수 있는 경우의 수 x 3 -> dp[i] = dp[i-2] * 3 (i>=4, 2씩 증가)
- 특수 모양을 만들 수 있는 칸을 2칸씩 늘리면서 만들 수 있는 경우의 수 -> dp[i] += dp[j] * 2 (j <= i-4, 2씩 차감)
public class Problem_3xnTiling {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 8;
solution(n);
}
public static int solution(int n) {
int answer = 0;
int mod = 1000000007;
long[] dp = new long[5001];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[2] = 3;
for(int i=4; i<=n; i+=2){
dp[i] = dp[i-2] * 3;
for(int j=i-4; j>=0; j-=2){
dp[i] += dp[j] * 2;
}
dp[i] = dp[i] % mod;
}
answer = (int) dp[n];
return answer;
}
}
이번 문제는 같이 문제를 풀었던 형의 도움 덕분에 dp문제 해결을 위한 단계 설립을 다시 한번 깨달을 수 있었다. dp는 한 두가지의 기준이 될만한 요소를 찾고, 그 기준을 기반으로 규칙을 나열하면 점화식이 나올 수 있다는 것을 알았다.
[가장 먼 노드]
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/49189
코딩테스트 연습 - 가장 먼 노드
6 [[3, 6], [4, 3], [3, 2], [1, 3], [1, 2], [2, 4], [5, 2]] 3
programmers.co.kr
* 조건
- 노드의 개수 n과 간선의 연결 정보가 주어진다
- 2 <= n <= 20000, 1 <= 간선의 개수 <= 50000
- 간선은 양방향이다
- 가장 멀리 떨어져 있는 노드들의 개수를 구한다
- 시작 노드는 1이다
* 알고리즘
- 인접한 곳을 탐색: BFS
* 로직(Logic)
- 인접 행렬 or 인접 리스트를 만든다
- 루트 노드부터 인접한 노드를 큐에 넣는다
- 인접한 노드들을 다 넣은 순간이 하나의 level -> 마지막으로 큐가 비어있다면 탐색을 시작한 시점의 level이 마지막 단계이다
- 즉, 해당 level에 존재했던 큐의 사이즈를 출력하면 된다
<인접 행렬>
import java.util.*;
class AdjMatrix {
public int nodeNum;
public boolean[][] matrix;
public AdjMatrix(int nodeNum) {
this.nodeNum = nodeNum;
matrix = new boolean[nodeNum+1][nodeNum+1];
}
public void makeMatrix(int v1, int v2){
matrix[v1][v2] = true;
matrix[v2][v1] = true;
}
}
class Solution {
static boolean[] checked;
static AdjMatrix adjMatrix;
public int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
int answer = 0;
adjMatrix = new AdjMatrix(n);
for(int i=0; i<edge.length; ++i){
int v1 = edge[i][0];
int v2 = edge[i][1];
for(int j=0; j<edge.length; ++j){
adjMatrix.makeMatrix(v1, v2);
}
}
//bfs 진행
checked = new boolean[n+1];
int startNode = 1;
answer = doProcess(startNode, n);
return answer;
}
private static int doProcess(int startNode, int n) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
checked[startNode] = true;
queue.offer(startNode);
int size = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
size = queue.size();
for(int s=0; s<size; ++s){
int q = queue.poll();
//인접한 노드 찾기
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
if(!checked[i] && adjMatrix.matrix[q][i] == true){
queue.offer(i);
checked[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
return size;
}
}
<인접 리스트>
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Problem_FarNode {
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>();
static boolean[] checked;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 6;
int[][] edge = {
{3, 6}, {4, 3}, {3, 2}, {1, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 4}, {5, 2}
};
int answer = solution(n, edge);
System.out.println(answer);
}
public static int solution(int n, int[][] edge) {
int answer = 0;
//인접리스트 생성
adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i){
adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int[] e : edge){
int v1 = e[0];
int v2 = e[1];
adjList.get(v1).add(v2);
adjList.get(v2).add(v1);
}
int startNode = 1;
checked = new boolean[n+1];
answer = doBfs(startNode);
return answer;
}
private static int doBfs(int startNode) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(startNode);
checked[startNode] = true;
int size = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
size = queue.size();
for(int s=0; s<size; ++s){
int q = queue.poll();
for(int node : adjList.get(q)){
if(!checked[node]){
queue.offer(node);
checked[node] = true;
}
}
}
}
return size;
}
}'Algorithm > Problem_프로그래머스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스(디스크 컨트롤러, 섬 연결하기) - Java (0) | 2019.11.06 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스(단어 변환, 예산) - Java (0) | 2019.11.04 |
| 프로그래머스(타일 장식물, 4단 고음) - Java (0) | 2019.10.30 |
| 프로그래머스(자물쇠와 열쇠) - Java (0) | 2019.10.29 |
| 프로그래머스(카카오 프렌즈 컬러링북, N으로 표현) - Java (0) | 2019.10.25 |